Snark
A snark is a connected bridgeless cubic graph (i.e., a biconnected cubic graph) with edge chromatic number of four. (By Vizing's theorem, the edge chromatic number of every cubic graph is either three or four, so a snark corresponds to the special case of four.) Snarks are therefore class 2 graphs.
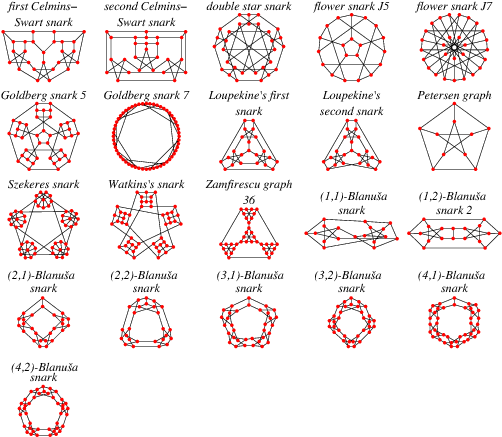
In order to avoid trivial cases, snarks are commonly restricted to be connected (so that the graph union of two Petersen graphs is excluded), have girth 5 or more and not to contain three edges whose deletion results in a disconnected graph, each of whose components is nontrivial (Read and Wilson 1998, p. 263).
Snarks that are trivial in the above senses are sometimes called "reducible" snarks. A number of reducible snarks are illustrated above.
The Petersen graph is the smallest snark, and Tutte conjectured that all snarks have Petersen graph graph minors. This conjecture was proven in 2001 by Robertson, Sanders, Seymour, and Thomas, using an extension of the methods they used to reprove the four-color theorem. All snarks are necessarily nonplanar and nonhamiltonian.
The Petersen graph remained the only known snark until 1946, when the Blanuša snarks were published (Blanuša 1946). Tutte discovered the next snark, which was rediscovered together with a number of related snarks by Blanche Descartes. Szekeres (1973) found a fifth snark, Isaacs (1975) proved there was an infinite family of snarks, and Martin Gardner (1976) proposed that the name "snarks" be given to these graphs. Of the smaller snarks, there is one with 10 vertices (the Petersen graph), two with 18 vertices (the Blanuša snarks), six with 20 vertices (of which one is the flower snark), and 20 with 22 vertices.
The double star snark has 30 vertices, and the Szekeres snark has 50 vertices. Goldberg found
an additional class of snarks. Additional snarks include the two Celmins-Swart snarks
on 26 vertices (Read and Wilson 1998, p. 281), the first and second Loupekine's
snarks on 22 vertices (Read and Wilson 1998, p. 279) and Watson's snark on 50
vertices (Read and Wilson 1998, p. 281). Note that the flower snarks ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() are illustrated
incorrectly by Read and Wilson (1998, pp. 276 and 281-282).
are illustrated
incorrectly by Read and Wilson (1998, pp. 276 and 281-282).
The numbers of nontrivial snarks on ![]() , 12, 14, ...
nodes are 1, 0, 0, 0, 2, 6, 20, 38, 280, 2900, ... (OEIS A130315;
Brinkmann and Steffen 1998). Royle maintains an enumeration of nontrivial snarks
up to 28 vertices, which is the search limit obtained by Brinkmann and Steffen (1998).
, 12, 14, ...
nodes are 1, 0, 0, 0, 2, 6, 20, 38, 280, 2900, ... (OEIS A130315;
Brinkmann and Steffen 1998). Royle maintains an enumeration of nontrivial snarks
up to 28 vertices, which is the search limit obtained by Brinkmann and Steffen (1998).
The following table summarizes some named snarks.

 snark
snark